SSK focuses on experiential architecture that integrates the form and meaning inherent in space by utilizing data and systems. SSK implements adaptive architecture, an active methodology that transcends the physical limitations of space and ensures a healthy living environment through the optimal balance of form and function. It aims to revitalize fragmented daily life through refined spatialization of intangible elements that affect spatial psychology, such as light, shadow, sound, and fluid dynamics. As a high-end studio that performs comprehensive design from furniture and lighting, which are the basic units of architecture, to detailed design and supervision, SSK does not accept low-cost projects or meaningless prolific works. As a design-oriented studio that pursues the pinnacle of architectural detail through dense study, SSK continues to work on innovative spaces.
SSK 는 공간에 담긴 조형과 의미를 데이터와 시스템에 기반하여 통합하는 실증적인 건축을 추구합니다. 형상과 기능의 최적화된 균형을 통해 공간이 지닌 물리적 한계를 극복하고 건강한 정주환경을 보장하는 능동적인 건축방법론인 Adaptive Architecture (환경적응건축)을 지향합니다. 이는 공간심리에 영향을 미치는 빛, 음영, 소리, 유체 등 무형요소의 정제된 공간화를 통해 파편화된 일상을 재생하는데 목적이 있습니다. 건축의 기본단위인 가구와 라이팅부터 실시설계 및 공사감리까지 종합디자인을 수행하는 High-end Studio 로 저가수주 및 무의미한 다작은 하지 않습니다. 밀도있는 스터디를 통해 건축 디테일의 정점을 추구하는 Design-oriented Studio 로 혁신적인 공간작업을 이어가고 있습니다.
Environmentally
Adaptive Architecture
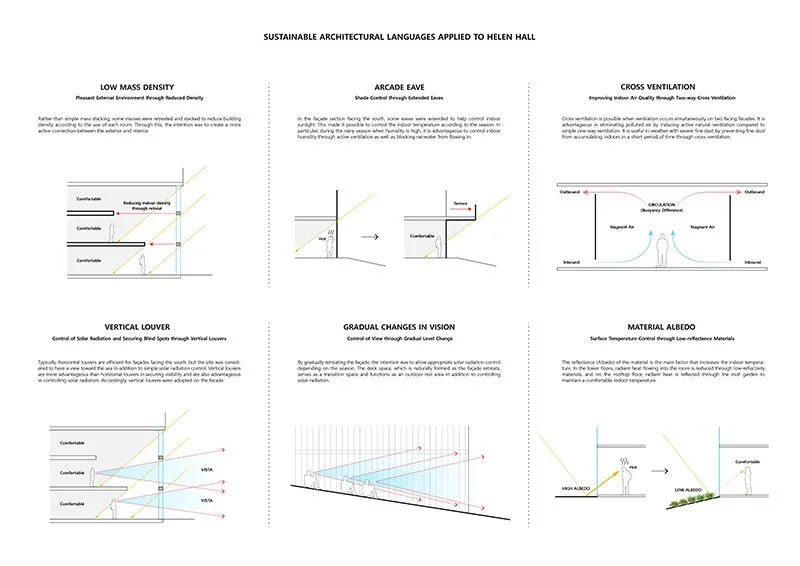
SSK pursues environmentally optimised architectural forms that respond sensitively to local microclimates within rapidly expanding high-density urban contexts such as London, Berlin, and Seoul. From this standpoint, we reconsider the role of architecture as a social medium—one that realises both spatial sustainability and public value. In particular, there is an urgent need to establish robust sustainable design strategies for high-density Asian cities such as Seoul, South Korea, which faces the risk of secondary environmental pollution due to transboundary CO₂ emissions and its geopolitical position. In addition, SSK operates at the intersection of art and architecture. We believe architecture serves as a vital mediator between society and nature. In our continual search for authenticity and truth within society, we have delivered projects of diverse scales and typologies, with a particular focus on public, memorial, and sustainable architecture. It is our firm conviction that sustainable methodologies capable of generating high-quality spaces offer the most effective solutions for our clients. Accordingly, SSK integrates principles of sustainability and public engagement from the earliest stages of conceptual design.
First, to achieve the technical realisation of sustainability, we undertake a range of environmental analyses to identify architectural forms that ensure long-term performance. These include seasonal indoor thermal mass analysis, solar radiation studies based on building surface materiality, and CFD simulations in relation to built form, among others. Through these methods, we determine building forms and site plans that demonstrate optimal thermal efficiency for the selected context. Second, to secure public engagement, we simulate optimal movement patterns by combining preference analysis—grounded in psychological research such as prospective cohort studies and survey sampling—with behavioural pattern analysis based on psychological states within public spaces. Through this dual methodological approach, SSK is able to derive the most objective and context-responsive solutions for each site. We consciously avoid dogmatic architectural forms driven by rigid or uncritical adherence to predefined concepts. Instead, we seek adaptive alternative schemes through optimal coding, positioning architecture as a collaborative medium that operates within defined regulatory frameworks while remaining responsive to society.
SSK는 런던, 베를린, 서울과 같이 지속적으로 확장되는 고밀도 현대 도시 환경에서 지역 미기후에 적응하는 환경 최적화 건축 형태를 추구합니다. 이러한 관점을 바탕으로, 우리는 건축을 사회적 매개체로서 재정의하며 공간적 지속가능성과 공공성을 동시에 실현하고자 합니다. 특히 CO₂ 배출에 따른 국경 간 환경 영향과 지리적 조건으로 인해 2차 환경오염의 위험에 노출된 한국 서울과 같은 고밀도 아시아 도시를 위해, 보다 강력하고 전략적인 지속가능 건축 디자인의 필요성이 대두되고 있습니다. 또한 SSK는 예술과 건축의 경계를 넘나드는 실천을 지향합니다. 우리는 건축이 사회와 자연을 연결하는 핵심적인 매개체라고 믿습니다. 사회 속에서의 진정성과 본질적 가치를 탐구해 온 SSK는 다양한 규모와 유형의 프로젝트를 수행해 왔으며, 특히 공공건축, 기념건축, 지속가능 건축 분야에 주력해 왔습니다. 양질의 공간을 창출하는 지속가능한 설계 방법론만이 고객에게 제공할 수 있는 최적의 해법이라는 것이 우리의 확고한 신념입니다. 이에 따라 SSK는 개념 설계 초기 단계부터 지속가능성과 공공성을 설계의 핵심 원리로 반영합니다.
첫째, 지속가능성을 기술적으로 구현하기 위해 다양한 환경 분석을 수행합니다. 계절별 실내 열용량 분석, 건축 외피 재료에 따른 일사량 분석, 건축 형태에 따른 CFD(전산유체역학) 분석 등 다각적인 시뮬레이션을 통해 지속가능성을 보장하는 건축 형태를 도출합니다. 이러한 분석 과정을 통해 대상 부지에서 최적의 열효율을 확보할 수 있는 건축 형태와 배치 계획을 결정합니다. 둘째, 공공성을 확보하기 위해 심리학적 연구에 기반한 선호도 분석(전향적 Cohort Study, 설문 조사 등)과 공공 공간에서의 심리 상태에 따른 행태 패턴 분석을 결합하여 최적의 동선 체계를 시뮬레이션합니다. 이러한 이중 분석 방법론을 통해 SSK는 각 부지의 맥락에 가장 객관적이고 합리적인 해법을 도출합니다. 우리는 개념에 대한 맹목적 집착이나 과도하게 규정된 정의에 의해 형성되는 교조적인 건축 형태를 지양합니다. 대신, 정해진 제도적 틀 안에서 사회와 협력하는 매개체로서 건축이 기능할 수 있도록, 최적화된 코딩을 통해 조정된 대안 계획을 지속적으로 탐색합니다.
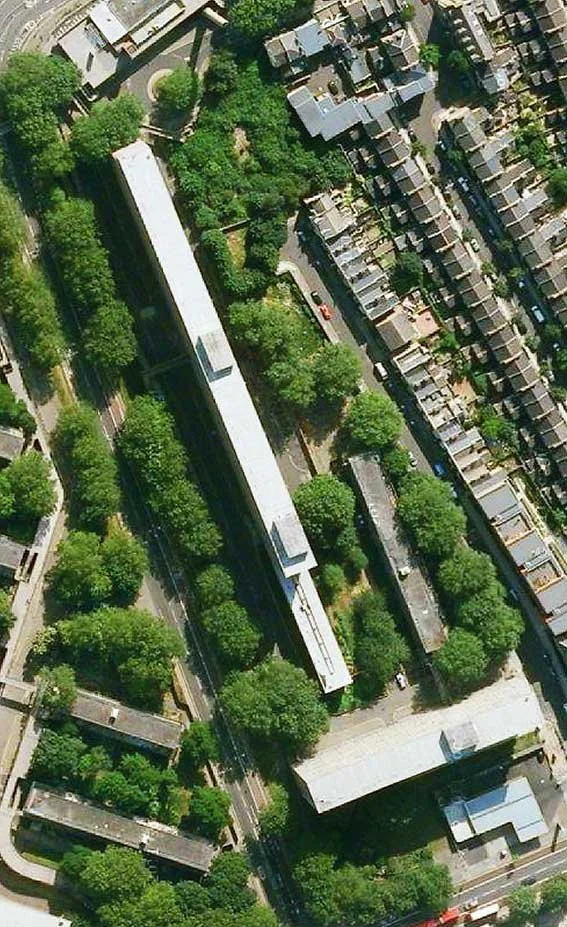
Precedent-1
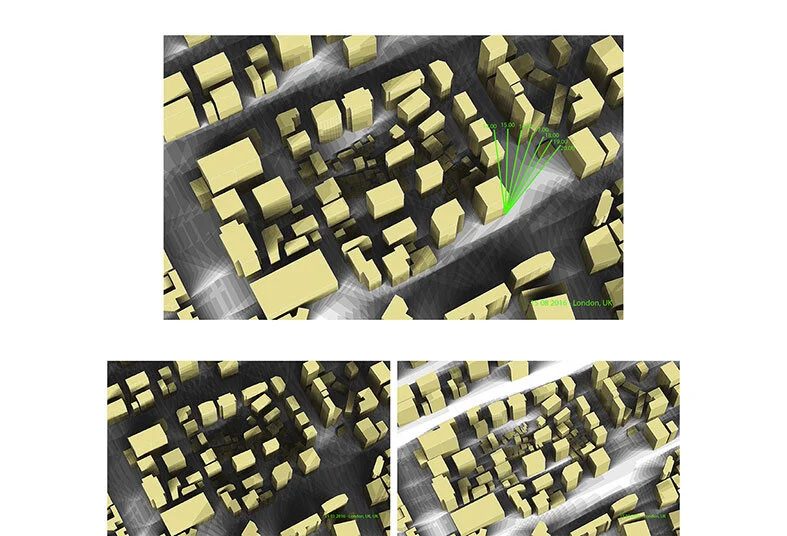
Heygate Estate Regeneration (London, United Kingdom)
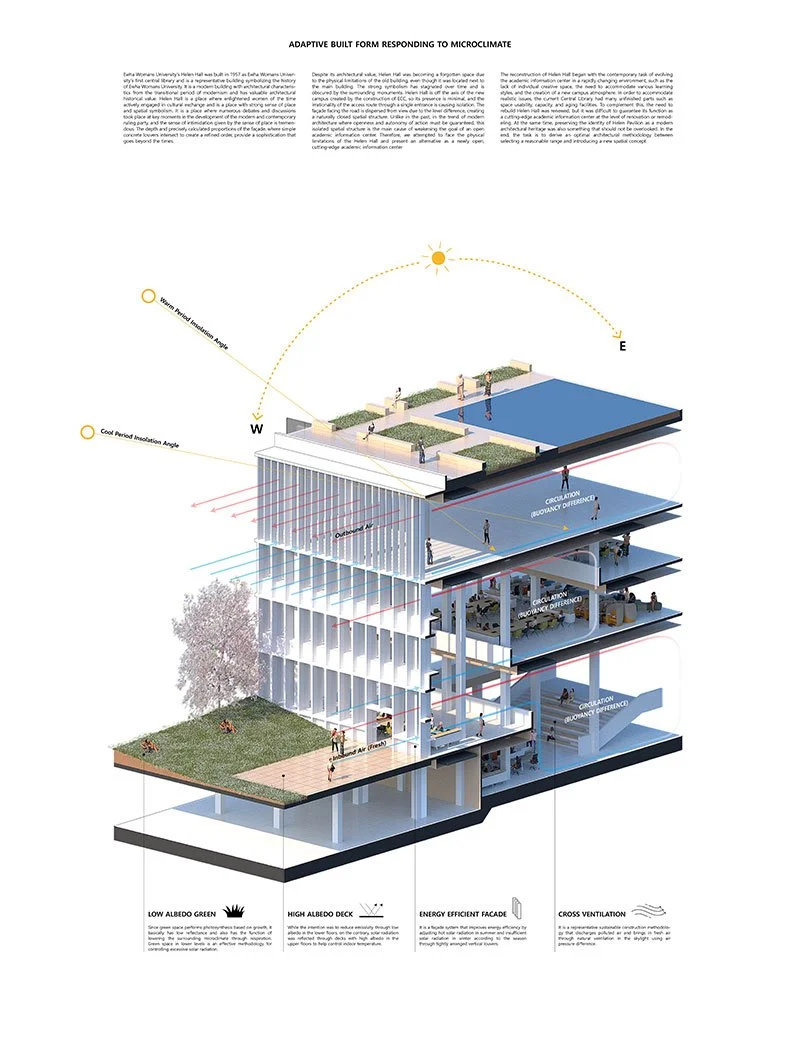
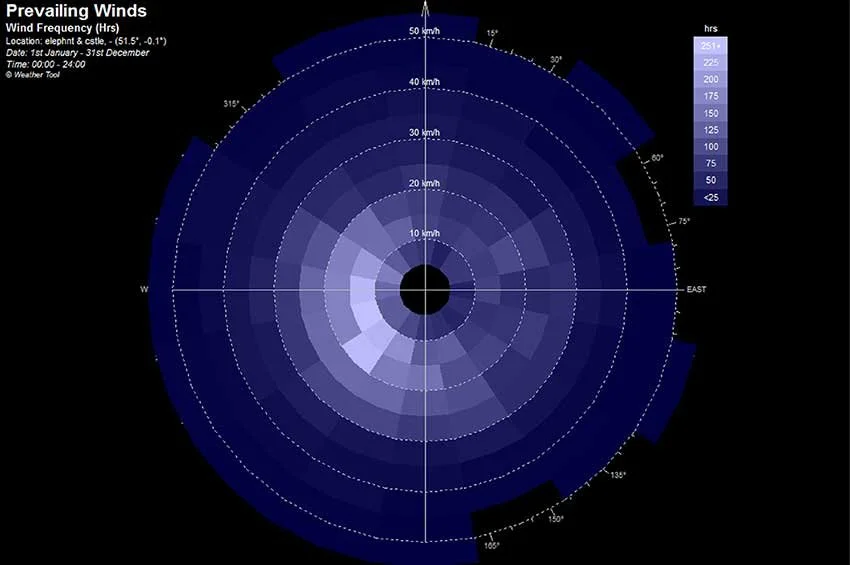
We integrate sustainability and public value from the earliest stages of the conceptual design process, ensuring that environmental performance and social responsibility are embedded as fundamental design drivers rather than supplementary considerations. To this end, a comprehensive series of environmental analyses is undertaken at the outset in order to identify architectural typologies capable of delivering long-term sustainability and spatial quality. These analyses include seasonal indoor thermal mass studies to evaluate thermal stability and energy efficiency, solar radiation assessments based on the materiality and configuration of the building envelope, and wind tunnel simulations using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) to examine airflow patterns and microclimatic behaviour in relation to building form. By synthesising these analytical processes, we are able to assess the environmental performance of design alternatives with a high degree of accuracy. Through detailed microclimatic environmental analysis, optimal thermal efficiency and environmental responsiveness for the specific site are established. The results directly inform the determination of building form, orientation, and spatial layout, allowing the architecture to respond precisely to local climatic conditions while maximising environmental comfort and long-term sustainability.
우리는 개념 설계 초기 단계부터 지속가능성과 공공성을 핵심 설계 원리로 통합하여, 환경적 성능과 사회적 책임이 부가적인 요소가 아닌 설계의 근간으로 작동하도록 합니다. 이를 위해 설계 초기 과정에서부터 장기적인 지속가능성과 공간의 질을 동시에 확보할 수 있는 건축 유형을 도출하기 위한 종합적인 환경 분석을 수행합니다. 주요 분석 항목으로는 계절별 실내 열질량(열용량) 분석을 통한 열적 안정성과 에너지 효율 평가, 건축 외피의 재료 구성과 형태에 따른 일사 및 복사열 분석, 그리고 건축 형태에 따른 공기 흐름과 미기후 특성을 검토하기 위한 전산유체역학(CFD) 기반 풍동 시뮬레이션이 포함됩니다. 이러한 다층적인 분석 과정을 종합함으로써, 설계 대안의 환경적 성능을 보다 정밀하고 객관적으로 평가할 수 있습니다. 정밀한 미기후 환경 분석을 통해 대상 부지에 최적화된 열효율과 환경 대응 전략을 도출하고, 그 결과를 바탕으로 건축의 형태, 배치, 방향성 및 공간 구성 전반을 결정합니다. 이를 통해 건축은 지역 기후 조건에 능동적으로 반응하는 동시에, 쾌적한 환경 성능과 장기적인 지속가능성을 실현하는 공간으로 완성됩니다.
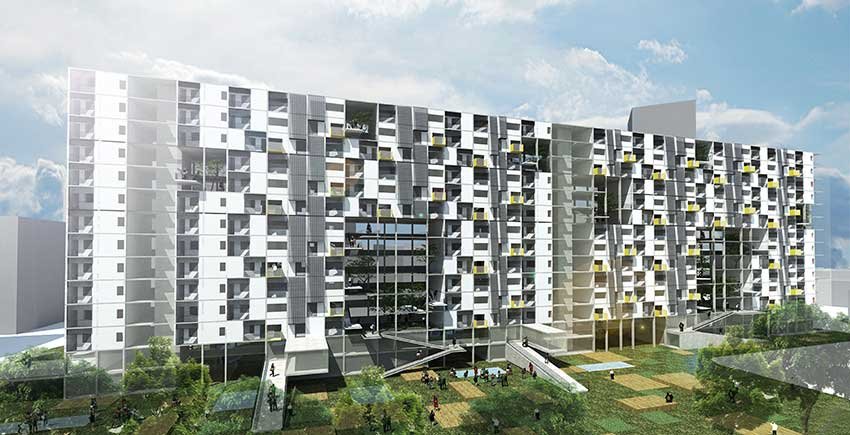






Precedent-2
Sustainable Built Forms Theory in High-density Urban Area (Seoul, South Korea)
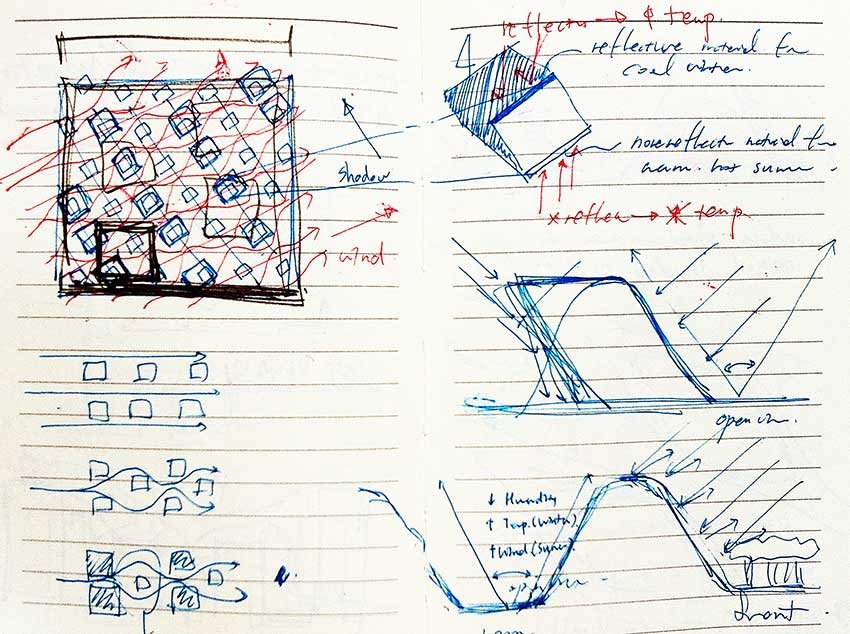
We simulate user behaviour patterns that can be realistically implemented on the site through a comprehensive analysis of residents’ preferences, informed by psychological research methods such as prospective cohort studies and survey sampling. In parallel, we examine behavioural patterns in public spaces in relation to varying psychological states, allowing us to understand how users interact with and inhabit shared environments over time. By synthesising these qualitative and quantitative analyses, we are able to translate complex social dynamics into spatial strategies that are both contextually grounded and socially responsive. Through a process of restrained architectural design coding, we deliberately avoid excessive formal expression, instead pursuing carefully calibrated alternatives that harmonise with the surrounding urban and natural context. This approach enables our architecture to reflect and reinforce the sense of place while remaining adaptable to the needs and behaviours of its users.
우리는 전향적 코호트 연구와 설문 조사 등 심리학적 연구 방법에 기반한 거주자 선호도 분석을 통해, 실제 부지에 구현 가능한 사용자 행태 패턴을 시뮬레이션합니다. 이와 동시에 공공 공간에서 나타나는 다양한 심리 상태에 따른 행태 패턴을 분석함으로써, 시간이 흐름에 따라 사용자가 공간을 인식하고 점유하는 방식에 대한 심층적인 이해를 구축합니다. 이러한 정성적·정량적 분석을 종합하여 복합적인 사회적 역동성을 공간 전략으로 전환하고, 맥락에 기반한 사회적 대응형 설계를 도출합니다. 과도한 조형적 표현을 지양하는 절제된 건축 디자인 코딩 과정을 통해, 주변의 도시 및 자연 환경과 조화를 이루며 장소성을 반영하는 정제된 대안 설계를 모색합니다. 이를 통해 건축은 사용자 행태에 유연하게 대응하는 동시에, 지역 고유의 정체성과 맥락을 강화하는 매개체로 기능합니다.

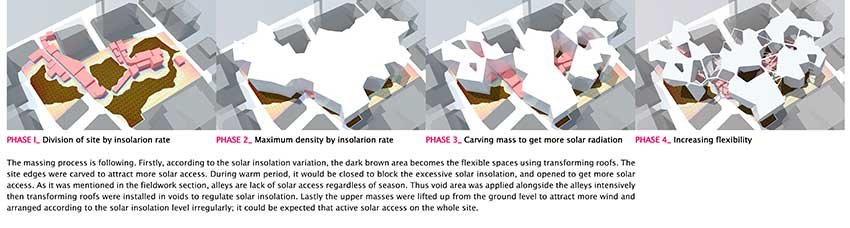
Design Phase-1
CFD Analysis
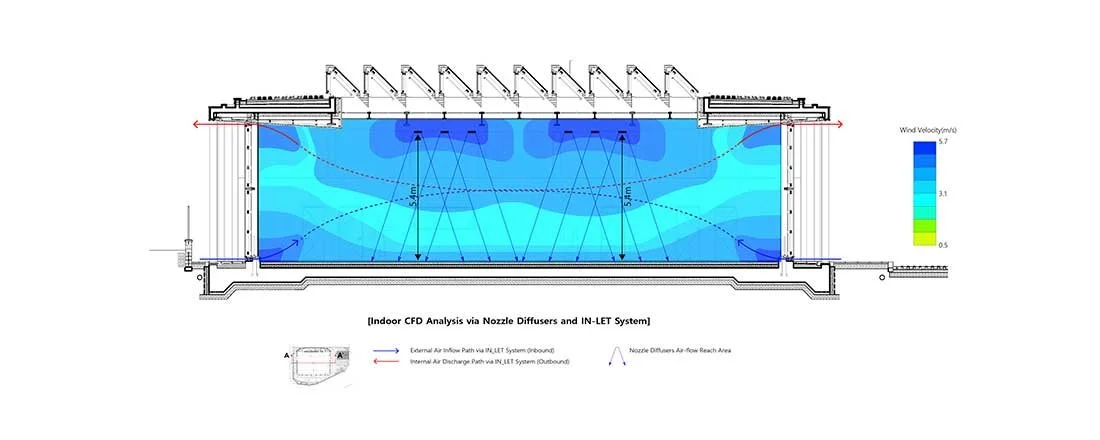
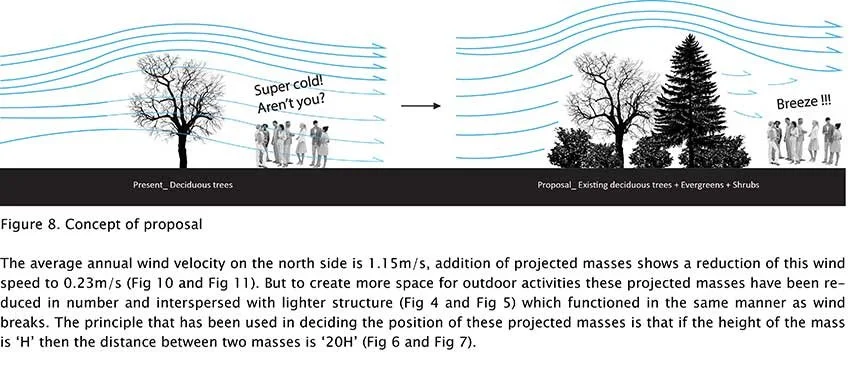
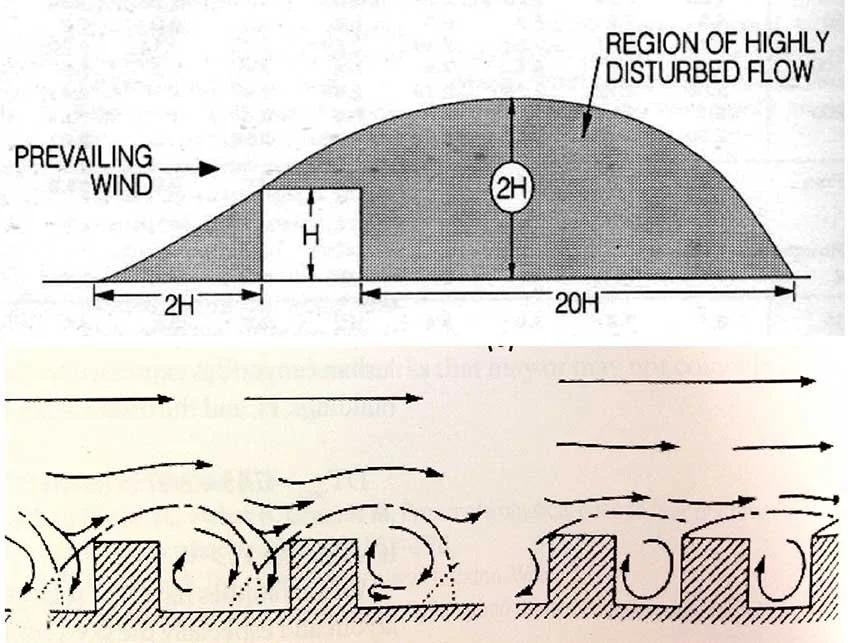
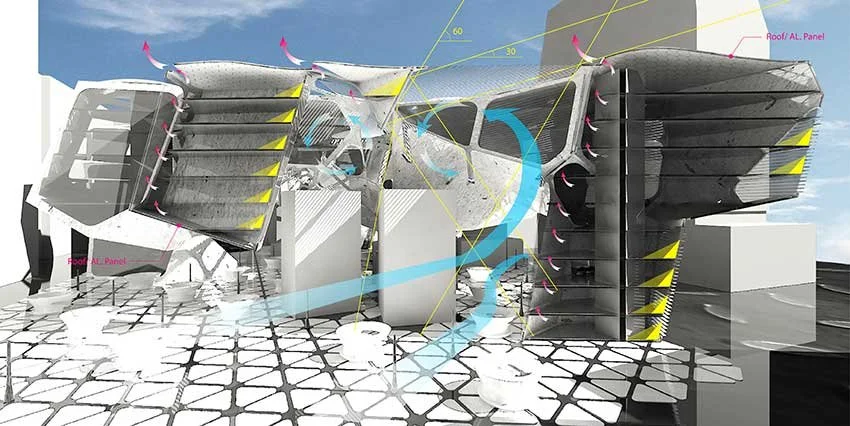
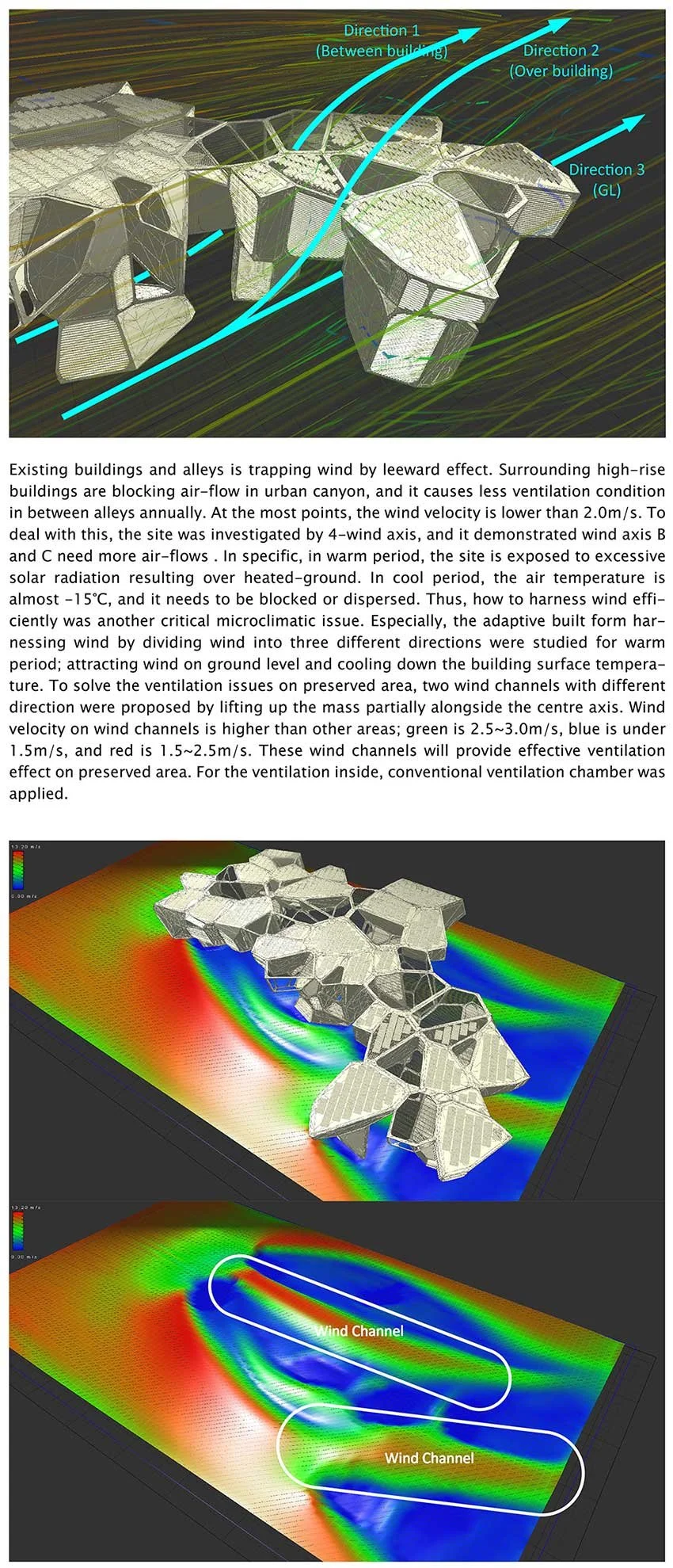
We conduct in-depth analyses of airflow within high-density urban environments using computational fluid dynamics (CFD), supported by a range of advanced environmental simulation and analysis tools. This approach enables a detailed understanding of wind behaviour, pressure distribution, natural ventilation potential, and microclimatic interactions that emerge from the complex spatial relationships between buildings in dense urban fabrics. By examining these aerodynamic and environmental factors, we are able to evaluate how different building forms influence urban ventilation, heat dissipation, and pedestrian-level comfort. The analytical outcomes provide a quantitative basis for optimising architectural massing and orientation in order to mitigate heat accumulation and improve environmental performance at both the building and urban scales. Based on these findings, we derive energy-efficient building forms that are carefully calibrated to the climatic conditions of Korea, a region characterised by four distinct seasons with significant variations in temperature, humidity, and wind patterns. By aligning architectural form with seasonal environmental performance, our design strategy reduces reliance on mechanical systems, enhances passive ventilation, and ensures stable energy efficiency throughout the year. As a result, architecture becomes an active environmental system that contributes to long-term sustainability and resilience within high-density urban contexts.
우리는 전산유체역학(CFD)을 기반으로 한 정밀한 공기 흐름 분석을 통해 고밀도 도시 환경에서 발생하는 풍환경을 심층적으로 연구하며, 이를 위해 다양한 고급 환경 시뮬레이션 및 분석 도구를 활용합니다. 이러한 접근은 밀집된 도시 조직 속에서 건축물 간의 복합적인 공간 관계로 인해 형성되는 바람의 거동, 압력 분포, 자연 환기 가능성, 그리고 미기후 상호작용을 체계적으로 이해할 수 있도록 합니다. 공기역학적·환경적 요소에 대한 분석을 통해, 서로 다른 건축 형태가 도시 차원의 환기 성능, 열 축적 완화, 보행자 레벨의 열적·환경적 쾌적성에 어떠한 영향을 미치는지를 정량적으로 평가합니다. 이러한 분석 결과는 건축 매스의 구성과 방향성을 최적화하기 위한 객관적인 근거로 작용하며, 건축 단위와 도시 단위를 아우르는 환경 성능 향상 전략으로 확장됩니다. 이와 같은 연구를 바탕으로, 기온·습도·풍향이 계절별로 크게 변화하는 사계절 기후를 지닌 한국의 환경 조건에 정밀하게 대응할 수 있는 에너지 효율적 건축 형태를 도출합니다. 계절별 환경 성능을 고려한 건축 형태 전략은 기계 설비에 대한 의존도를 낮추고 수동적 환기 성능을 극대화하며, 연중 안정적인 에너지 효율을 확보하도록 합니다. 이를 통해 건축은 고밀도 도시 맥락 속에서 장기적인 지속가능성과 환경적 회복력을 적극적으로 구현하는 능동적인 환경 시스템으로 기능하게 됩니다.
Design Phase-2
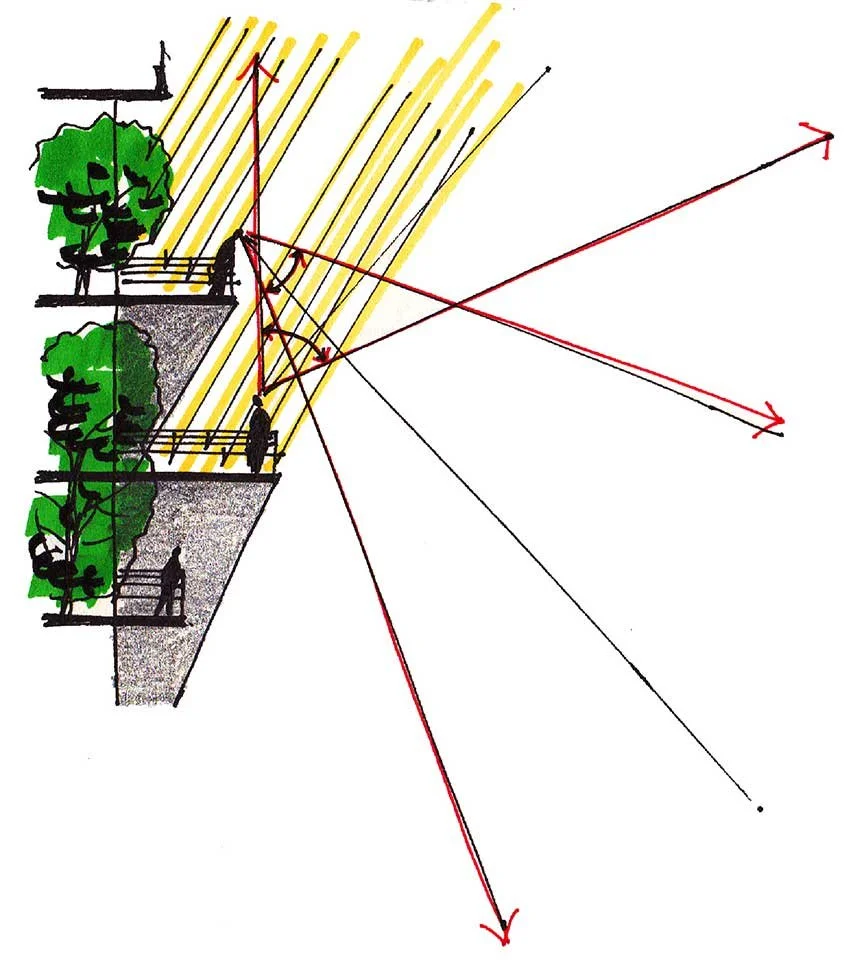
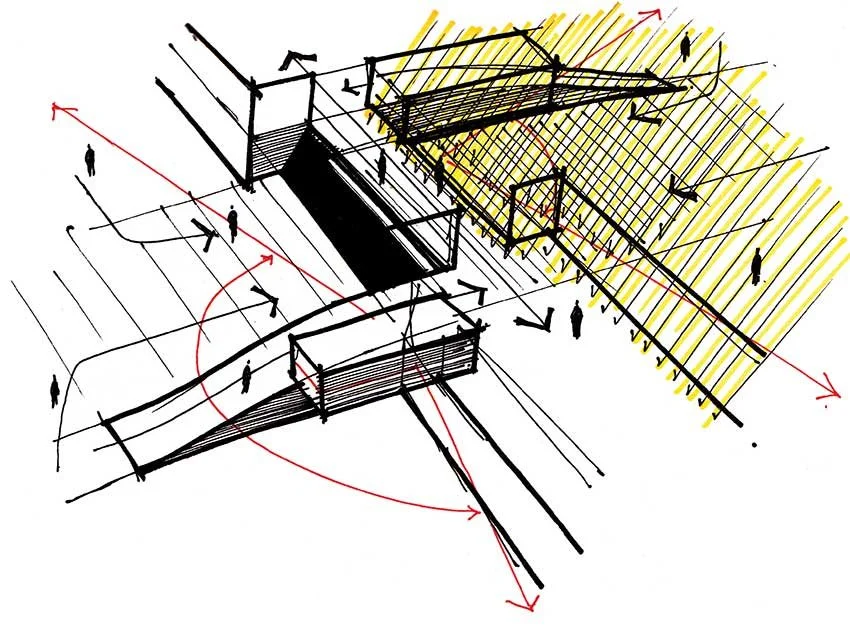
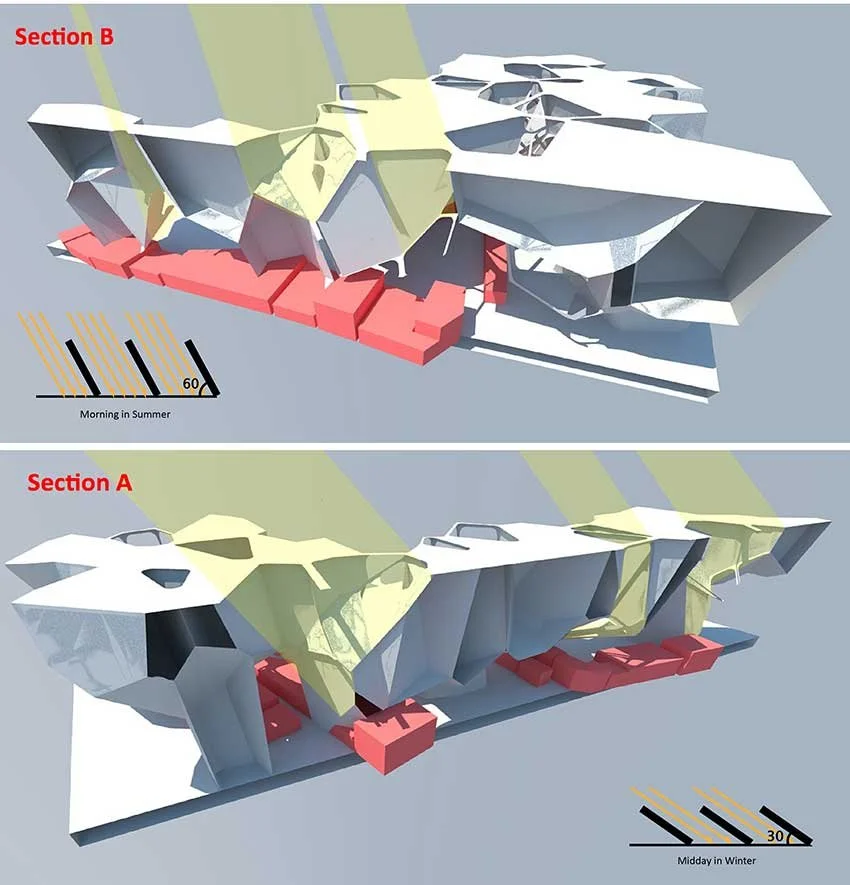
Seasonal Shading Analysis
Shading analysis is carried out using specialised environmental simulation tools such as Ecotect and Geco, enabling us to assess how building orientation, massing, and façade design influence solar gain and, consequently, heating and cooling loads. By modelling the sun’s path and its interaction with the building envelope throughout the year, we can identify areas of excessive solar exposure as well as opportunities for passive shading and daylight optimisation. This analytical process allows us to understand the seasonal variations in solar radiation and their impact on indoor thermal comfort and energy consumption. Through iterative simulations, we evaluate multiple design alternatives, adjusting façade geometry, overhangs, and orientation to achieve an optimal balance between natural daylighting and solar protection. The resulting insights provide a clear basis for determining the most energy-efficient building form suited to Korea’s climate, which is characterised by four distinct seasons with significant fluctuations in temperature, humidity, and solar intensity. By integrating shading strategies from the early design stage, we are able to reduce reliance on mechanical cooling and heating systems, enhance passive environmental control, and improve overall building performance throughout the year. This approach supports our broader commitment to sustainable design, ensuring that architecture responds intelligently to local climatic conditions while maximising occupant comfort and energy efficiency.
Ecotect, Geco 등과 같은 전문 환경 분석 프로그램을 활용한 차양 분석을 통해 건물의 방향, 매스, 파사드 설계가 일사량에 어떠한 영향을 미치며 그 결과 난방 및 냉방 부하에 어떤 차이를 발생시키는지 정밀하게 평가합니다. 연중 태양의 경로와 건물 외피와의 상호작용을 모델링함으로써 과도한 일사 노출이 발생하는 지점과 수동적 차양 및 자연채광 최적화가 가능한 지점을 동시에 파악할 수 있습니다. 이러한 분석 과정은 계절별 일사량 변화가 실내 열적 쾌적성과 에너지 소비에 미치는 영향을 체계적으로 이해하는 데 도움을 줍니다. 반복적인 시뮬레이션을 통해 다양한 설계 대안을 검토하며, 파사드 형상, 처마 및 돌출부, 건물 방향 등을 조정하여 자연채광과 일사 차단 사이의 최적 균형을 도출합니다. 그 결과는 기온·습도·일사 강도가 계절별로 크게 변하는 사계절 기후의 한국 환경에 가장 적합한 에너지 효율적 건축 형태를 결정하는 명확한 근거가 됩니다. 설계 초기 단계부터 차양 전략을 통합함으로써 기계식 냉·난방 시스템에 대한 의존도를 낮추고, 수동적 환경 제어 능력을 향상시키며, 연중 전반적인 건물 성능을 개선할 수 있습니다. 이러한 접근은 지역 기후 조건에 지능적으로 대응하는 지속가능한 설계를 구현함으로써, 사용자 쾌적성과 에너지 효율을 동시에 극대화하는 데 기여합니다.
Design Phase-3
Micro-CFD Analysis
Using computational fluid dynamics (CFD), we analyse the airflow around and along the building envelope to understand how wind patterns and air movement influence heating and cooling loads. This analysis examines the interaction between the building skin and its surrounding environment, including the effects of wind pressure, turbulence, and convective heat transfer. By evaluating these aerodynamic factors, we can identify areas of the façade that are most susceptible to heat gain or loss, and how ventilation strategies can be optimised to improve overall thermal performance. Through a process of iterative simulation and refinement, we test multiple design alternatives to determine the most effective building form for reducing energy consumption. The results enable us to optimise façade geometry, orientation, and material selection in order to achieve enhanced thermal comfort and energy efficiency. This approach is particularly relevant to Korea’s climate, which is characterised by four distinct seasons with significant variations in temperature, humidity, and wind conditions. By aligning building form with local climatic behaviour, we are able to derive an optimised architectural solution that reduces reliance on mechanical systems and supports long-term sustainability.
전산유체역학(CFD)을 활용하여 건축 외피 주변 및 외피를 따라 흐르는 공기 흐름을 분석함으로써, 풍동 패턴과 공기 이동이 난방 및 냉방 부하에 어떠한 영향을 미치는지 정밀하게 파악합니다. 이 분석은 건물 외피와 주변 환경 간의 상호작용, 즉 풍압, 난류, 대류 열 전달 등의 영향을 포함하여 평가합니다. 이러한 공기역학적 요소를 통해 외피에서 열 취득 또는 열 손실이 가장 크게 발생하는 지점을 식별하고, 환기 전략을 어떻게 최적화할 수 있는지에 대한 근거를 도출할 수 있습니다. 반복적인 시뮬레이션과 설계 수정 과정을 통해 여러 설계 대안을 검토하며 에너지 소비를 최소화할 수 있는 최적의 건축 형태를 도출합니다. 그 결과는 외피 형상, 방향성, 재료 선정 등을 최적화하여 실내 열적 쾌적성과 에너지 효율을 동시에 향상시키는 데 활용됩니다. 이는 기온·습도·풍환경이 계절별로 크게 변화하는 한국의 사계절 기후 조건에서 특히 중요한 접근 방식입니다. 지역 기후의 특성을 고려한 건축 형태 전략을 통해 기계 설비에 대한 의존도를 줄이고, 장기적인 지속가능성을 지원하는 최적화된 건축 솔루션을 마련할 수 있습니다.
Design Phase-4
Urban Daylight Analysis
Daylight analysis evaluates the amount and quality of sunlight entering the building, and assesses how this solar exposure influences heating and cooling loads over the course of the year. By modelling the sun’s path and its interaction with the building envelope, we are able to quantify the distribution of natural light within interior spaces, identify areas of excessive solar gain, and evaluate the potential for glare or overheating. This enables a more precise understanding of how daylight contributes to both energy consumption and occupant comfort. Through iterative simulations, we test various design options—including window-to-wall ratios, façade articulation, shading devices, and internal layout strategies—to achieve an optimal balance between natural illumination and thermal performance. The insights gained from daylight analysis inform decisions on building orientation, massing, and façade configuration, ensuring that the design makes efficient use of daylight while minimising the need for artificial lighting and mechanical cooling. This approach is particularly pertinent to Korea’s climate, which is characterised by four distinct seasons with significant fluctuations in temperature and solar intensity. By aligning the building form with seasonal daylight conditions, we derive an energy-efficient architectural solution that reduces reliance on mechanical systems, improves indoor environmental quality, and enhances overall sustainability throughout the year.
일조 분석은 건물 내부로 유입되는 햇빛의 양과 질을 평가하고, 이러한 일사량이 연간 난방 및 냉방 부하에 어떠한 영향을 미치는지를 분석합니다. 태양의 경로와 건물 외피와의 상호작용을 모델링함으로써 실내 공간 내 자연광 분포를 정량적으로 파악하고, 과도한 일사로 인한 열 취득이 발생하는 영역을 식별하며, 눈부심이나 과열 가능성을 평가할 수 있습니다. 이를 통해 일조가 에너지 소비와 거주자의 쾌적성에 미치는 영향을 보다 정확하게 이해할 수 있습니다. 반복적인 시뮬레이션을 통해 창문 비율, 파사드의 형태적 구성, 차양 장치, 내부 공간 배치 전략 등 다양한 설계 대안을 검토하며 자연채광과 열적 성능 간 최적의 균형을 도출합니다. 일조 분석에서 얻은 통찰은 건물의 방향성, 매스 구성, 외피 설계 결정에 반영되어, 인공조명과 기계식 냉방 의존도를 최소화하면서 일조를 효율적으로 활용할 수 있도록 합니다. 이러한 접근은 기온과 일사 강도가 계절별로 크게 변하는 사계절 기후의 한국 환경에서 특히 중요합니다. 계절별 일조 조건에 맞춘 건축 형태 전략을 통해 기계 설비에 대한 의존도를 줄이고, 실내 환경 품질을 개선하며, 연중 지속가능성을 향상시키는 에너지 효율적 건축 솔루션을 도출합니다.
Design Phase-5
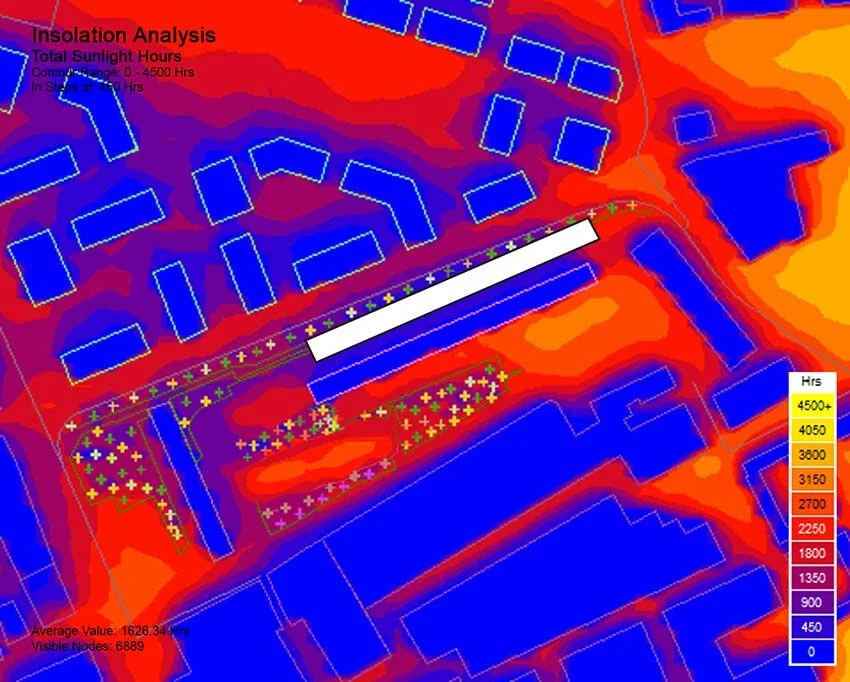
Seasonal Insolation Analysis
We analyse the amount of sunlight that influences heating and cooling loads through seasonal solar radiation studies. By modelling the sun’s trajectory and its interaction with the building envelope across different times of the year, we can accurately quantify solar exposure and identify how it varies between seasons. This enables us to understand the impact of solar gain on thermal comfort and energy consumption, and to determine which areas of the building are most affected by heat gain or loss. Through iterative simulation and design refinement, we evaluate multiple architectural options—such as orientation, massing, façade composition, and shading strategies—to achieve the most effective balance between natural daylighting and thermal performance. The insights derived from seasonal solar radiation analysis inform decisions regarding building form, envelope design, and spatial configuration, ensuring that the building responds appropriately to varying climatic conditions throughout the year. This approach is particularly significant in Korea, where the climate is characterised by four distinct seasons with substantial differences in temperature, humidity, and solar intensity. By aligning the building form with seasonal solar conditions, we are able to derive an optimised architectural solution that reduces energy consumption, enhances indoor comfort, and supports long-term sustainability in a highly variable climate.
우리는 계절별 일사 분석을 통해 난방 및 냉방 부하에 영향을 미치는 일사량을 정밀하게 평가합니다. 태양의 궤적과 건물 외피와의 상호작용을 연중 다양한 시점에서 모델링함으로써, 계절에 따라 변화하는 일사 노출을 정확히 정량화할 수 있습니다. 이를 통해 일사로 인한 열 취득이 열적 쾌적성과 에너지 소비에 미치는 영향을 이해하고, 열 취득 또는 열 손실이 특히 큰 건물 영역을 식별할 수 있습니다. 반복적인 시뮬레이션과 설계 개선 과정을 통해 건물의 방향, 매스 구성, 외피 설계, 차양 전략 등 여러 설계 대안을 검토하며 자연채광과 열적 성능 사이의 최적 균형을 도출합니다. 계절별 일사 분석에서 얻은 통찰은 건축 형태, 외피 구성, 공간 배치 결정에 반영되어 연중 변화하는 기후 조건에 맞춰 건축이 적절히 대응하도록 합니다. 이러한 접근은 기온·습도·일사 강도가 계절별로 크게 달라지는 한국의 사계절 기후에서 특히 중요합니다. 계절별 일사 조건에 맞춘 건축 형태 전략을 통해 에너지 소비를 줄이고 실내 쾌적성을 높이며, 변동성이 큰 기후 속에서도 장기적인 지속가능성을 확보하는 최적화된 건축 솔루션을 도출할 수 있습니다.